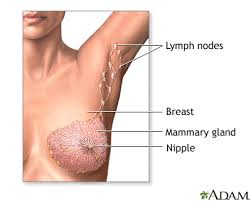
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the breast tissue. It occurs when abnormal cells in the breast grow and multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor.
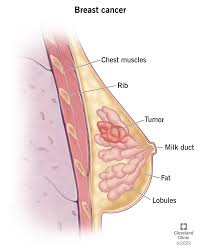
Types of Breast Cancer
1. Ductal Carcinoma: Begins in the milk ducts
2. Lobular Carcinoma: Begins in the milk-producing glands (lobules)
3. Invasive Breast Cancer: Spreads to surrounding tissues
4. Non-Invasive Breast Cancer: Remains in the original location
5. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Lacks three common receptors (estrogen, progesterone, and HER2)
6. HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: Has high levels of HER2 protein
7. Inflammatory Breast Cancer: A rare and aggressive type
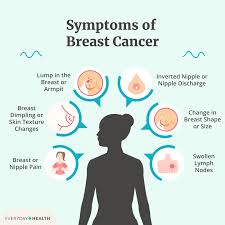
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
- New Lump or Thickening: In the breast or underarm area
- Change in Size or Shape: Of the breast
- Dimpling or Redness: Of the skin
- Nipple Discharge: Other than milk
- Change in Nipple Position: Inversion or retractions
- Pain or Tenderness: In the breast or underarm area
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Underarm or near the breastbone
Causes of Breast Cancer
- Genetics: Family history and inherited mutations (BRCA1 and BRCA2)
- Hormonal Factors: Estrogen exposure and reproductive history
- Radiation Exposure: Previous radiation therapy
- Dense Breasts: Higher risk for women with dense breasts
- Lifestyle Factors: Alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, and obesity
Health Implications of Breast Cancer
1. Metastasis: Cancer spreads to other parts of the body
2. Recurrence: Cancer returns after treatment
3. Mortality: Breast cancer is a leading cause of cancer deaths
4. Emotional and Psychological Impact: Anxiety, depression, and body image issues
5. Financial Burden: Treatment costs and lost productivity

people at a higher risk of developing breast cancer
1. Women: Breast cancer is more common in women than men.
2. Family History: Those with a first-degree relative (parent, child, or sibling) diagnosed with breast cancer.
3. Genetic Mutations: Carriers of BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations.
4. Previous Breast Cancer: Women who have had breast cancer in one breast are at higher risk of developing it in the other breast.
5. Dense Breasts: Women with dense breasts are at higher risk.
6. Age: Risk increases with age, especially after 40.
7. Radiation Exposure: Women who have received radiation therapy to the chest area.
8. Reproductive History: Women who started menstruating early or entered menopause late.
9. Body Weight: Being overweight or obese after menopause.
10. Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle.
11. Alcohol Consumption: Drinking alcohol in excess.
12. Hormone Replacement Therapy: Women who have used hormone replacement therapy for an extended period.
13. Women with a History of Certain Breast Conditions: Such as lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) or atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH).
Testing for breast cancer typically involves a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and biopsies.
Here are the common methods:
1. Clinical Breast Exam (CBE): A healthcare professional examines your breasts, looking for lumps, thickening, or changes in size or shape.
2. Mammography: An X-ray exam that uses low-energy radiation to produce detailed images of the breasts.
3. Digital Mammography: A type of mammography that uses digital technology to produce images.
4. 3D Mammography (Tomosynthesis): A type of mammography that uses low-dose X-rays to produce 3D images.
5. Ultrasound: Uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the breasts.
6. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Uses strong magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images.
7. Biopsy: A procedure to remove tissue or cells from the breast for examination.
8. Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB): Uses a thin needle to collect cells from the breast.
9. Core Needle Biopsy (CNB): Uses a thicker needle to collect tissue from the breast.
10. Stereotactic Biopsy: Uses mammography to guide the biopsy needle.
11. MRI-Guided Biopsy: Uses MRI to guide the biopsy needle.
12. Genetic Testing: Analyzes genes for mutations that increase breast cancer risk.
prevention of Breast Cancer
1. Healthy Diet: Focus on whole, nutrient-rich foods
2. Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per day
3. Maintain Healthy Weight: Excess weight increases risk
4. Limit Alcohol Consumption: No more than one drink per day
5. Don’t Smoke: Smoking increases risk
6. Breastfeeding: Can lower risk in premenopausal women
7. Avoid Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): If possible
8. Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours per night
9. Manage Stress: Chronic stress may increase risk
10. Get Regular Screenings: Mammograms, clinical exams, and self-exams
11. Know Your Family History: If you have a strong family history, consider genetic testing
12. Avoid Exposure to Chemicals: Limit exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, and other harmful substances
13. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water
14. Get Enough Vitamin D: Maintain adequate levels through sun exposure, supplements, or fortified foods
15. Avoid Radiation Exposure: Limit exposure to radiation from medical imaging tests like mammograms and CT scans.